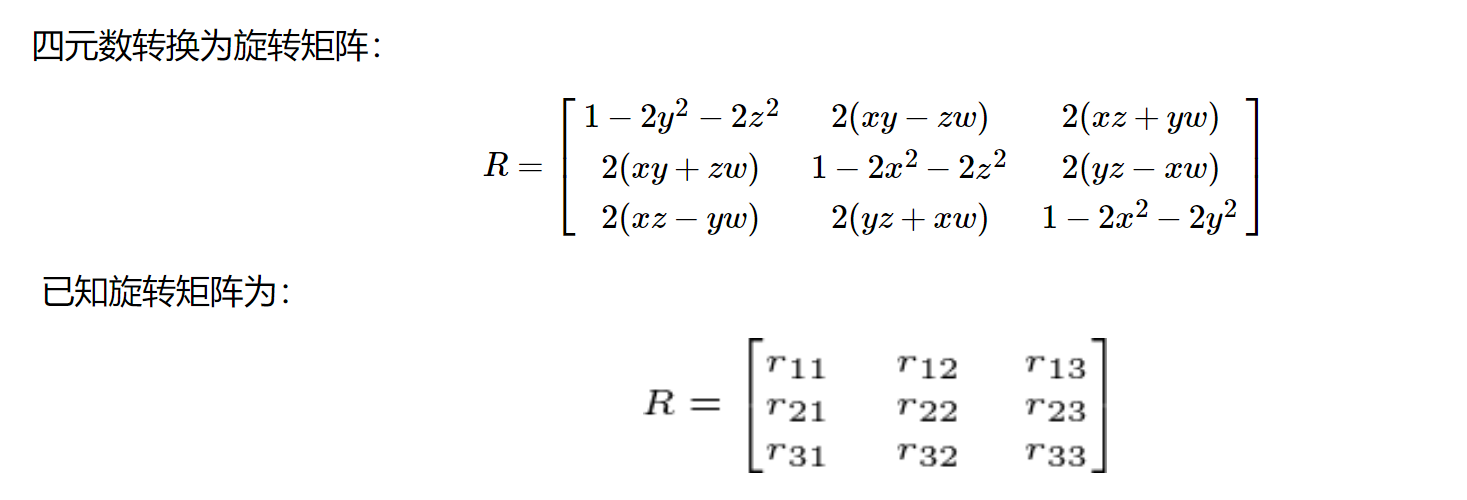本周总结 主要工作总结
2023.07.24 调参 rewards:soft_dof_limit [0.9],base_height_target [0.25]
scales:trac_lin_vel [1.0],trac_ang_vel [0.5],lin_vel_z [-2.0],dof_acc [-2.5e-7],ang_vel_xy [-0.05],action_rate [-0.01],torques [-2e-4],dof_pos_limits [-10.0]
total steps:1500
初始参数 [0.9, 0.25; 1.5, 0.75; -2.0, -1.25e-7, -0.025, -0.02, -1e-4 , -10.0]
减少 torques [0.9, 0.25; 1.5, 0.75; -2.0, -1.25e-7, -0.025, -0.02, (-5e-5, -2.5e-5 ), -5.0]
观察到 -5e-5 ,-2.5e-5 的 rew_torques 曲线在 100 步时下沉依次减半,收敛时数值依次减半;rew_action_rate 曲线和 rew_ang_vel_xy 曲线在 100 时下沉更多,收敛时两曲线重合数值同为原曲线两倍
GitHub - lucas-maes/learning-legged-locomotion: Learning Legged Locomotion project for the course Robot Learning - IFT6163
2023.07.25 阅读文献 Learning Quadruped Locomotion using Bio-Inspired Neural Networks with Intrinsic Rhythmicity
什么是循环神经网络? | IBM
循环神经网络 (Recurrent Neural Network, RNN) - 范叶亮 | Leo Van
Hidden Layer 的神经元状态同时依赖输入和上一时刻的神经元状态
Understanding LSTM Networks | colah’s blog
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Recurrent Neural Networks
2023.07.26 Isaac Gym 单个机器人测试 create gym / create sim / create env / load ground / load asset / prepare sim
give command (slide bar in the viewer)
get observation $\rightarrow$ policy $\rightarrow$ action
apply torque
simulate
camera attached
文献检索 MPC-guided RL / RL-based MPC 2023.07.27 机体系下的重力单位方向向量 (欧拉角) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 def projectedGravity (gravity_world_frame, eul_ang ) -> np.ndarray(3,): """ 在机体系下表示重力单位方向向量; 注意欧拉角表示方式和旋转顺序 """ if not isinstance (gravity_world_frame, np.ndarray): gravity_world_frame = np.array(gravity_world_frame, dtype=np.float64) if not isinstance (eul_ang, np.ndarray): eul_ang = np.array(eul_ang, dtype=np.float64) eul_ang = -eul_ang.reshape(-1 ) invRX = np.array([[1 , 0 , 0 ], [0 , np.cos(eul_ang[0 ]), -np.sin(eul_ang[0 ])], [0 , np.sin(eul_ang[0 ]), np.cos(eul_ang[0 ])]], dtype=np.float64) invRY = np.array([[np.cos(eul_ang[1 ]), 0 , np.sin(eul_ang[1 ])], [0 , 1 , 0 ], [-np.sin(eul_ang[1 ]), 0 , np.cos(eul_ang[1 ])]], dtype=np.float64) invRZ = np.array([[np.cos(eul_ang[2 ]), -np.sin(eul_ang[2 ]), 0 ], [np.sin(eul_ang[2 ]), np.cos(eul_ang[2 ]), 0 ], [0 , 0 , 1 ]], dtype=np.float64) invRM = np.dot(invRX, np.dot(invRY, invRZ)) gravity_local_frame = np.dot(invRM, gravity_world_frame.reshape(-1 )) return gravity_local_frame
本质上是求坐标系变换的 (逆) 矩阵
一般对于旋转矩阵(3*3),旋转向量 / 角轴(3*1),四元数(4*1),我们给定一串数字,就能表示清楚一个姿态 / 旋转
但如果我给出一组欧拉角(后面都是指 Tait–Bryan angles,绕 $x,y,z$ 三个轴的转角分别为 $(α,β,γ)$,我们不能能确定一个明确的姿态.需要再追加两个属性:
旋转顺序
内旋/外旋.才能确定的给出这组欧拉角对应的姿态.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation as Rdef projectedGravityR (gravity_world_frame, eul_ang ): if not isinstance (gravity_world_frame, np.ndarray): gravity_world_frame = np.array(gravity_world_frame, dtype=np.float64) if not isinstance (eul_ang, np.ndarray): eul_ang = np.array(eul_ang, dtype=np.float64) r = R.from_euler('xyz' , eul_ang.reshape(-1 )) invRotM = np.linalg.inv(r.as_matrix()) gravity_local_frame = np.dot(invRotM, gravity_world_frame.reshape(-1 )) return gravity_local_frame
机体系下的重力单位方向向量 (四元数)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def projectedGravityOri (gravity_world_frame, orientation ): """ 在机体系下表示重力单位方向向量 orientation = (x,y,z,w) """ x, y, z, w = orientation RHam = np.array([[1 -2 *y*y-2 *z*z, 2 *(x*y-z*w), 2 *(x*z+y*w)], [2 *(x*y+z*w), 1 -2 *x*x-2 *z*z, 2 *(y*z-x*w)], [2 *(x*z-y*w), 2 *(y*z+x*w), 1 -2 *x*x-2 *y*y]], dtype=np.float64) invRHam = np.linalg.inv(RHam) gravity_local_frame = np.dot(invRHam, gravity_world_frame.reshape(-1 )) return gravity_local_frame
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 if __name__ == "__main__" : rot = np.pi/4 eul_list = [rot, rot, rot] eul_ang = np.array(eul_list) gravity_world_frame = np.array([0 , 0 , -1 ]) projected_gravity = projectedGravity(gravity_world_frame, eul_ang) projected_gravity_R = projectedGravityR(gravity_world_frame, eul_ang) print (projected_gravity) print (projected_gravity_R) eul = R.from_euler('xyz' , eul_ang, degrees=False ) orientation = eul.as_quat() projected_gravity_Ori = projectedGravityOri(gravity_world_frame, orientation) print (projected_gravity_Ori)
欧拉角的旋转顺序能改变吗 | 知乎 浅析机器人学位姿之单位四元数 四元数 (Quaternions) 四元数与旋转矩阵_四元数转旋转矩阵 | 冰激凌啊的博客 四元数与欧拉角 (RPY角) 的相互转换 | XXX已失联
2023.07.28 张量形式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 def projectedGravityOri (orientation ) -> torch.Tensor: """ 在机体系下表示重力单位方向向量; orientation = (x,y,z,w) """ gravity_world_frame = torch.tensor([0 , 0 , -1 ], dtype=torch.float ) x = np.array(orientation[:, 0 ]) y = np.array(orientation[:, 1 ]) z = np.array(orientation[:, 2 ]) w = np.array(orientation[:, 3 ]) RHam = torch.zeros(orientation.shape[0 ], 3 , 3 , dtype=torch.float ) RHam_ndarray = np.array([[1 - 2 *y*y - 2 *z*z, 2 *x*y - 2 *z*w, 2 *x*z + 2 *y*w], [2 *x*y + 2 *z*w, 1 - 2 *x*x - 2 *z*z, 2 *y*z - 2 *x*w], [2 *x*z - 2 *y*w, 2 *y*z + 2 *x*w, 1 - 2 *x*x - 2 *y*y]]) RHam = torch.tensor(RHam_ndarray, dtype=torch.float ).permute(2 , 0 , 1 ) invRHam = torch.linalg.inv(RHam) gravity_local_frame = torch.matmul(invRHam, gravity_world_frame) return gravity_local_frame
以及
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def projectedGravityR (eul_ang ): """ 在机体系下表示重力单位方向向量; 注意欧拉角表示方式 (roll/pitch/yaw) 和旋转顺序 (x/y/z 轴) """ gravity_world_frame = torch.tensor([0 , 0 , -1 ], dtype=torch.float ) if not torch.is_tensor(eul_ang): eul_ang = torch.tensor(eul_ang, dtype=torch.float ) r = R.from_euler('xyz' , eul_ang) invRotM = torch.linalg.inv(torch.tensor(r.as_matrix(), dtype=torch.float )) gravity_local_frame = torch.matmul(invRotM, gravity_world_frame) return gravity_local_frame
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 if __name__ == "__main__" : rot = np.pi/4 eul_list = [[rot, 0 , 0 ], [rot, rot, rot]] eul_ang = np.array(eul_list) projected_gravity_R = projectedGravityR(eul_ang) print (projected_gravity_R) eul = R.from_euler('xyz' , eul_ang, degrees=False ) orientation = eul.as_quat() projected_gravity_ori = projectedGravityOri(orientation) print (projected_gravity_ori)
pytorch入门:基础操作_pytorch基本操作 | 张十八员外的博客
创建张量 加载数据 自定义数据及 训练模型 保存和加载模型
pytorch 中常见的 tensor 操作 | 知乎
维度变换、数据填充等
Pytorch torch.Tensor 的 4 种乘法 | u013250861的博客
torch.mul(元素对应相乘)
torch.mm(满足矩阵结构的乘法)
torch.matmul(最后2个维度进行torch.mm操作)
pytorch 入门篇 1 创建 tensor_pytorch 创建 tensor | Dark universe的博客
PyTorch 张量(tensor)的秩,轴,形状(Rank, Axes, and Shape)的理解 张量的秩 | 程序之巅的博客
Pytorch 中的 View, Reshape, Permute | 知乎
ValueError: only one element tensors can be converted to Python scalars 解决办法 | 甜度超标°的博客
2023.07.29 任务
奖励函数的设定
plot (threading)
通过 Unitree 手柄进行指令输入
Legged Gym 奖励函数的程序设计
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def _prepare_reward_function (self ): self.reward_functions = [] self.reward_names = [] for name, scale in self.reward_scales.items(): if name=="termination" : continue self.reward_names.append(name) name = '_reward_' + name self.reward_functions.append(getattr (self, name))
Matplotlib 多线程绘图功能介绍 | 极客笔记
使用 pyqtgraph 进行 python 实时绘图 | 码农家园
python 多线程: Thread 类的用法 | liulanba 的博客
threading - 基于线程的并行 | Python 3.11.4 文档
multiprocessing - 基于进程的并行 | Python 3.11.4 文档
Plotting Serial Data from Arduino in Real Time with Python | ThePoorEngineer
Python 如何实时绘制数据 - 腾讯云开发者社区 | 腾讯云
数据可视化 Matplotlib 绘制实时数据图表 - 腾讯云开发者社区 | 腾讯云
Multiprocessing | Matplotlib 3.7.2 documentation
Python 中 multiprocessing 模块之 Pipe 管道 | 哦…的博客
如何使用 Matplotlib 实时绘制数据 | 知乎
详解如何使用 Python 绘制动图 | 解析 FuncAnimation 接口用法以及实践 | NumLock 桌的博客
Python __call__()方法
将实例变成可调用对象
动态动画 Matplotlib 的 FuncAnimation 使用解析 | 望天边星宿的博客
2023.07.30 阅读文献 Soccer
贝塞尔 (Bézier) 曲线 | Mister Zhu的博客 贝塞尔曲线图形原理和公式推导 | 命运之手的博客 贝塞尔曲线 总结 | 挨踢大侠的博客 贝塞尔曲线 (Bezier Curve) 原理、公式推导及 MATLAB 代码实现 | beijing_txr 的博客 Python 进程间数据交互的几种实现方式
2023.07.31 Go1 效果改进 一些需要关注的东西
两个模型
dt (经检查 legged gym 中自带)feet_air_time
$K_p, K_d$
Learning to Walk in Minutes Using Massively Parallel Deep Reinforcement Learning by Nikita Rudin (ETH Nvidia)
CPG-RL
dt Isaac Gym 中已经在 _prepare_reward_function 中默认乘以 self.dt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 def _prepare_reward_function (self ): """ Prepares a list of reward functions, whcih will be called to compute the total reward. Looks for self._reward_<REWARD_NAME>, where <REWARD_NAME> are names of all non zero reward scales in the cfg. """ for key in list (self.reward_scales.keys()): scale = self.reward_scales[key] if scale==0 : self.reward_scales.pop(key) else : self.reward_scales[key] *= self.dt
feet_air_time 初始值为 1.0
一些疑问 Learning to Walk in Minutes Using Massively Parallel Deep Reinforcement Learning by Nikita Rudin (ETH Nvidia) 中的参数和 Legged Gym 中所给出的 reward scale 并不一样
测试文件管理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - Logs - A1_flat - ANYmal_flat - Go1_rough - Go1_flat - Year-Month-Date_Obs(45)_non-base-vel_ - - Year-Month-Date_Obs(48)_non-base-vel_ - Good results (temp)
Isaac Gym Test A Single Robot Transferring Policies from Isaac Gym Preview Releases — isaacsim latest documentation
Isaac Gym 逆运动学解算 Docs: Isaac Gym / Programming / Tensor API / Physics State / Jacobians and Mass Matrices
Examples:
See Franka IK Picking (franka_cube_ik_osc.py, franka_nut_bolt_ik_osc.py) for an example of using the Jacobian tensor for inverse kinetics.
See Franka OSC for an example of using Jacobians and mass matrices for Operational Space Control.
PDF: iksurvey.pdf
机器人的运动学解——逆向运动学解 | 知乎 干货 | “逆运动学”——从操作空间到关节空间(上篇)| 知乎 A curated list of awesome NVIDIA Isaac Gym frameworks, papers, software, and resources Deep RL for MPC control of Quadruped Robot Locomotion